MultiPoint™ Pacing is safe: 93.6% freedom from system-related complications1 demonstrated by a prospective, multi-center, randomized, double-blinded clinical trial (IDE study: 506 patients in 49 centers)
MultiPoint™ Pacing is feasible: The IRON-MPP registry of 507 patients in 76 centers throughout Italy demonstrated that pacing the ability to provide MPP from 2 electrode locations with a good threshold and no PNS is feasible in the majority of patients2
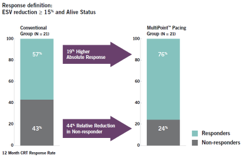
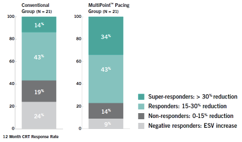
MultiPoint™ Pacing increases response rates: a single center randomized study of 44 patients demonstrated a 44% relative reduction in non-responders and a 19% higher absolute response as measured by reduction in ESV at 12 months3
References
1. Tomassoni, G., Baker II, J., Corbisiero, R., Love, C., Martin, D., Sheppard, R., Worley, S., Varma, N., Niazi, I. (2016). Safety and efficacy of multipoint pacing in cardiac resynchronization therapy: The MultiPoint Pacing (MPP) IDE Study. 2016 Heart Rhythm Society, LBCT 01-03
2. Forleo, G. B., Santini, L., Giammaria, M., Potenza, D., Curnis, A., Calabrese, V., . . . Zanon, F. (2016). Multipoint pacing via a quadripolar left-ventricular lead: Preliminary results from the Italian registry on multipoint left-ventricular pacing in cardiac resynchronization therapy (IRON-MPP). Europace, 1-8.
3. Pappone, C., Calovic, Z., Vicedomini, G., Cuko, A., McSpadden, L. C., Ryu, K., . . . Santinelli, V. (2015). Improving cardiac resynchronization therapy response with multipoint left ventricular pacing: twelve-month follow-up study. Heart Rhythm, 12, 1250-1258.
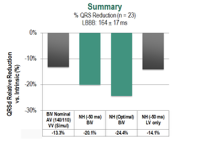
4. Wisnoskey, B. J., Cranke, G., Cantiion, D. J., & Varma, N. (2016). Feasibility of device-based electrical optimization via application of the negative AV hysteresis algorithm during cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT). Heart Rhythm Society